UNDERSTANDING JOINT PAIN
Joint pain is a common yet complex problem that can arise from various causes, ranging from acute injuries to chronic conditions like arthritis. It can affect any joint in the body, causing discomfort, pain, and stiffness. Understanding the specific cause of joint pain is critical for effective management and treatment. It's not just about treating the symptoms but also addressing the underlying cause, whether it's wear and tear, inflammation, infection, or an autoimmune disorder.

IDENTIFYING THE CAUSES OF JOINT PAIN
Joint pain can stem from numerous sources, including wear and tear of cartilage (osteoarthritis), autoimmune disorders (rheumatoid arthritis), crystal deposition (gout), overuse (tendinitis), and injuries (sprains and fractures). Each of these conditions has unique characteristics and treatments. For instance, osteoarthritis results from the breakdown of cartilage, while rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition where the body's immune system attacks its own tissues.
ARTHRITIS AS A PRIMARY CAUSE OF JOINT PAIN
Arthritis is one of the most common causes of joint pain, affecting millions worldwide. This group of diseases, which includes more than 100 different types, causes pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints. The most common forms are osteoarthritis, resulting from the wear and tear of joint cartilage, and rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder that affects the lining of the joints.
UNDERSTANDING THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF ARTHRITIS
ROLE OF INFLAMMATION IN JOINT PAIN
Inflammation is a critical component of many joint pain conditions, particularly arthritis. It's the body's natural response to injury or infection, but when it becomes chronic, it can lead to joint damage and pain. Managing inflammation through medication, lifestyle changes, and dietary modifications is essential for reducing pain and preventing further joint damage.

COMMON TYPES OF JOINT PAIN
Joint pain can vary greatly depending on the affected area. Common types include knee pain, often due to arthritis or injury; hip pain, which can be caused by arthritis or bursitis; and hand and finger joint pain, frequently a result of arthritis. Each type of joint pain requires a specific approach to diagnosis and treatment.
SYMPTOMS ACCOMPANYING JOINT PAIN
Along with pain, joint discomfort often includes symptoms like swelling, redness, warmth, stiffness, and a reduced range of motion. In some cases, joint pain can be accompanied by systemic symptoms like fever, weight loss, or fatigue, especially in autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. These symptoms can significantly impact a person's daily activities and quality of life.

EXERCISE AND JOINT PAIN
Regular exercise is crucial in managing joint pain. It helps by strengthening the muscles around the joints, improving flexibility, and reducing inflammation. Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, and walking are often recommended. It’s important to exercise within one's limits and avoid activities that might exacerbate joint pain.
LIFESTYLE, DIET, WEIGHT AND JOINT PAIN
EFFECTIVE TREATMENTS FOR JOINT PAIN
Effective treatment for joint pain depends on the underlying cause and may include medications such as anti-inflammatories or analgesics, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications like weight loss and exercise, and in severe cases, surgical intervention. The goal of treatment is not only to relieve pain but also to maintain joint function and prevent further damage.

PREVENTING JOINT PAIN
Prevention of joint pain involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and avoiding injuries. It's also important to manage chronic conditions like diabetes and heart disease, which can contribute to joint pain. Regular check-ups can help in the early identification and management of potential issues.
It is important to consult a healthcare professional if joint pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms like significant swelling, redness, or warmth around the joint, fever, or unexplained weight loss. These could indicate a more serious condition requiring professional medical intervention.
CHRONIC JOINT PAIN AND QUALITY OF LIFE
Chronic joint pain can significantly impact the quality of life, making everyday activities challenging and reducing overall well-being. Effective management, which may include a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and supportive therapies, is crucial in improving mobility, reducing pain, and enhancing the quality of life for those suffering from chronic joint pain.

GOUT IN FOOT
Gout, a form of arthritis, is caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in joints, often affecting the big toe. It results in intense pain, swelling, and redness. Treatment focuses on reducing uric acid levels in the blood with medications and dietary changes to avoid foods high in purines. During flare-ups, anti-inflammatory medications and pain relievers are used to manage symptoms.
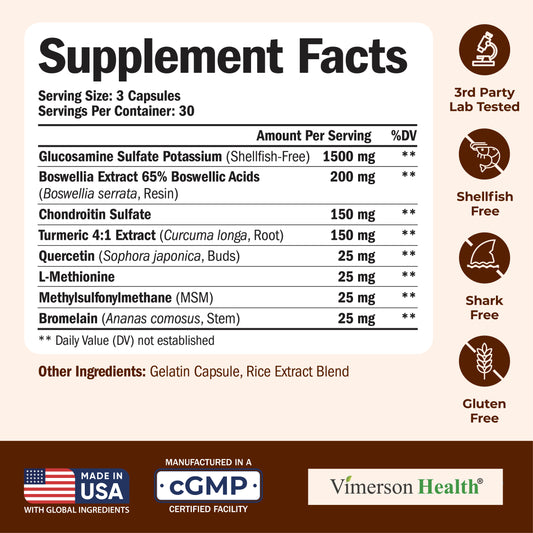
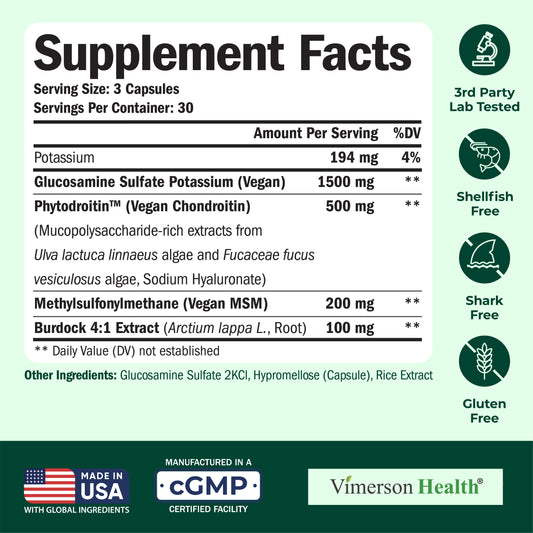
SUPPLEMENTS FOR BALANCING OCCASIONAL JOINT DISCOMFORT
Several supplements can help balance occasional joint discomfort, including Glucosamine, Chondroitin, and Fish Oil.* These supplements may help improve joint mobility and reduce occasional discomfort.* However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen, especially for those with existing health conditions or who are taking other medications.
BEST SUPPLEMENT FOR JOINT HEALTH🥇

Vimerson Health
Glucosamine Chondroitin MSM – Joint Support Supplement for Women and Men with Glucosamine Sulfate 1500 mg, Chondroitin and MSM – for Cartilage, Joint Health and Flexibility – 90 Capsules









* These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.