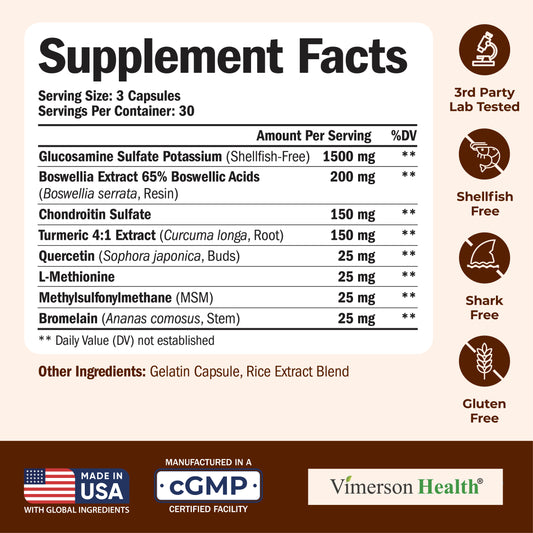
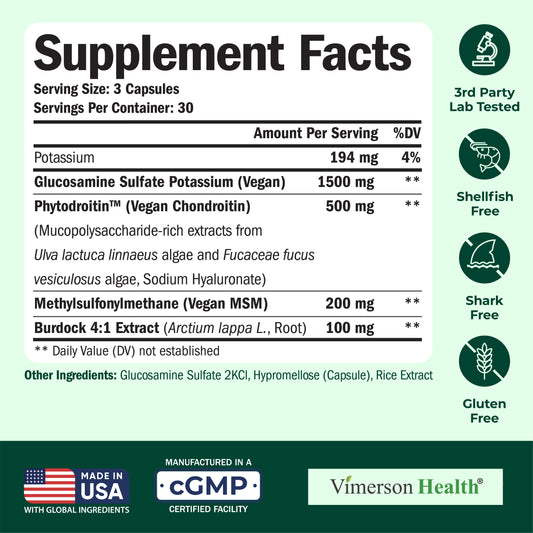
WHAT IS INFLAMMATION?
Inflammation is the body's instinctive response to injury or infection, a crucial part of the healing process. It signals the immune system to repair damaged tissue and defend against foreign invaders like bacteria and viruses. While acute inflammation is beneficial for health, chronic inflammation can contribute to various diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis. Understanding the difference between acute and chronic inflammation is essential for proper health management.

CAUSES OF INFLAMMATION IN THE BODY
The triggers of inflammation are diverse, including pathogens (bacteria and viruses), physical injuries (like cuts and bruises), and exposure to toxins or irritants. Chronic inflammation often results from long-term exposure to non-infectious agents like polluted air, a poor diet, or stress. Autoimmune disorders, where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, also contribute to chronic inflammation. Identifying and addressing these triggers is key to managing inflammation.
SYMPTOMS OF BODY INFLAMMATION
Inflammation symptoms can vary depending on whether the inflammation is acute or chronic. Acute inflammation typically causes pain, redness, swelling, and sometimes a loss of function in the affected area. Chronic inflammation may not have such obvious symptoms, often manifesting as fatigue, fever, mouth sores, abdominal pain, or chest pain. Recognizing these signs is crucial for early intervention and treatment.

THE ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DIET
An anti-inflammatory diet involves consuming foods that are known to reduce inflammation. This diet emphasizes fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, like berries and fatty fish, play a significant role in reducing inflammation. Conversely, it's advised to avoid or limit foods that can trigger inflammation, such as refined carbs, fried foods, and sugary beverages.
BEST ANTI-INFLAMMATORY FOODS
Certain foods are particularly effective in fighting inflammation. These include berries, like strawberries and blueberries, which are high in antioxidants. Fatty fish, such as salmon and mackerel, contain omega-3 fatty acids, known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Other beneficial foods include green leafy vegetables, nuts, and fruits like oranges and cherries. Incorporating these foods into your diet can significantly help in reducing inflammation.
EXERCISE, SLEEP AND STRESS: THE KEY OF INFLAMMATION
MANAGING GUT HEALTH TO REDUCE INFLAMMATION
Gut health is intricately linked to inflammation. A balanced gut microbiome is essential for maintaining a healthy immune response and thus managing inflammation. Consuming probiotics, found in yogurt and fermented foods, and prebiotics, found in foods like bananas and onions, can promote a healthy gut. A high-fiber diet also supports gut health, potentially reducing inflammation. Avoiding foods that disrupt gut balance, like high-sugar and processed foods, is also crucial.

HYDRATION AND INFLAMMATION
Staying well-hydrated is essential for overall health and can help in reducing inflammation. Water helps in flushing out toxins from the body, which can reduce inflammation. It also aids in the transportation of nutrients and oxygen to body cells, supporting the healing process. Drinking adequate amounts of water daily is an easy and effective way to help manage inflammation.
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY LIFESTYLE
HOW TO REDUCE INFLAMMATION QUICKLY
For immediate relief from acute inflammation, natural methods such as applying cold compresses to reduce swelling and elevating the affected area can be effective. For chronic inflammation, a more comprehensive approach involving dietary changes, regular exercise, and stress management is needed for long-term management. Quick fixes might provide temporary relief, but lifestyle changes are key for lasting results.

HOW TO PREVENT INFLAMMATION IN THE BODY
Preventing inflammation involves a holistic approach to health. This includes eating a balanced and anti-inflammatory diet, engaging in regular physical activity, ensuring adequate sleep, and managing stress levels. Additionally, avoiding known triggers such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and exposure to environmental toxins can help prevent inflammation. Regular health check-ups can also play a role in early detection and prevention.
DOES INFLAMMATION INCREASE WITH AGE?
BEST INFLAMMATION BALANCE SUPPLEMENTS
There are several natural supplements that can aid in balancing inflammation.* Turmeric, which contains curcumin, has potent inflammation balance and antioxidant properties.* Ginger, another powerful inflammation balance agent, can be taken in supplement form or used in cooking.* Omega-3 supplements, derived from fish oil or flaxseeds, are also effective in balancing inflammation.* However, it's important to consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen.
BEST SUPPLEMENT FOR INFLAMMATION BALANCE 🥇

Vimerson Health
Turmeric Curcumin Supplement with Ginger Root for Joint Support, Digestive & Gut Health - Contains Organic Turmeric Curcumin with Black Pepper (Bioperine) for Enhanced Absorption - 60 Capsules









* These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.